|
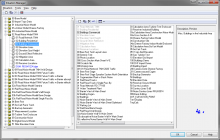
General Overview All geometry data or model objects is entered into Geo-Files or Layers. With one or more Geo-Files the user compiles a Situation. The Situation is the administrative units that represent either a planning stage (current status versus planned version in some years) or a noise type (road versus railway and industry noise). All non geometrical data are managed in standard databases formats so that an exchange of information to other programs can be accomplished with ease. The Geo-Database has predefined objects to characterize all model geometry and attributes necessary to describe the objects. The object can be broken down into:
|
|
Data Import and Management The Geo-Database import following data:
For project organization the user edits and compiltes the data in various layers to reduce redundancy of data. For example for most projects the topography is not changing so spot elevation and elevaiton lines can be in one Geo-Files. In the same project the difference between different models are additional noise sources or changing roads inputs. In those case we would have separate Geo-Files describing the parameters for each situation. Depending on the project the user decides on the structuring of the situation and the layers. Often times the objects that change from situation to situation and objects that stay the same throughout the project are organized in the same layers. The Situation Manager is an easy tool to compile layers for each situation and to document the content of each layer and describing the Situation. Aerial Photos or Bitmaps can be imported to digitize the geometry. An interface to Google Earth (Cartography Module) allows the import of geo-referenced aerial photos and Google Earth terrain elevation data. |
|
Model Verification The verification of the geometry and input parameters is crucial with increasing size of the noise model. The Geo-Database has numerous visual and tabular tools to verify the integrety of the noise model. The visual tools include:
Coordinate Operation, Attribute Explorer and Attribute Edior
Manipulation of Data
|
|
Object Input Each Geo-Database Object is pre-define. The geometry is entered with x, y and z coordinates. The object is either digitized (mouse, digitizer tablet) or imported. Each object has specific attribute to describe the geometry, coordinate, height, object identifier and technical attributes (i.e., sound power, idle pattern, absorption, building height, number of floors, ...). The attributes are used to characterize the relevant information for the noise or air pollution model or information that are of interest in terms of the assessment (recepter name, zoning, source name, group, number of occupants per house, ...) A object parameter window may have one to three tabs to allow the definition of the object attributes. |